The tomb of a priest dating back more than 4,400 years was discovered at the site of Saqqara, near Cairo, by an Egyptian archaeological mission, authorities announced on December 15, 2018.
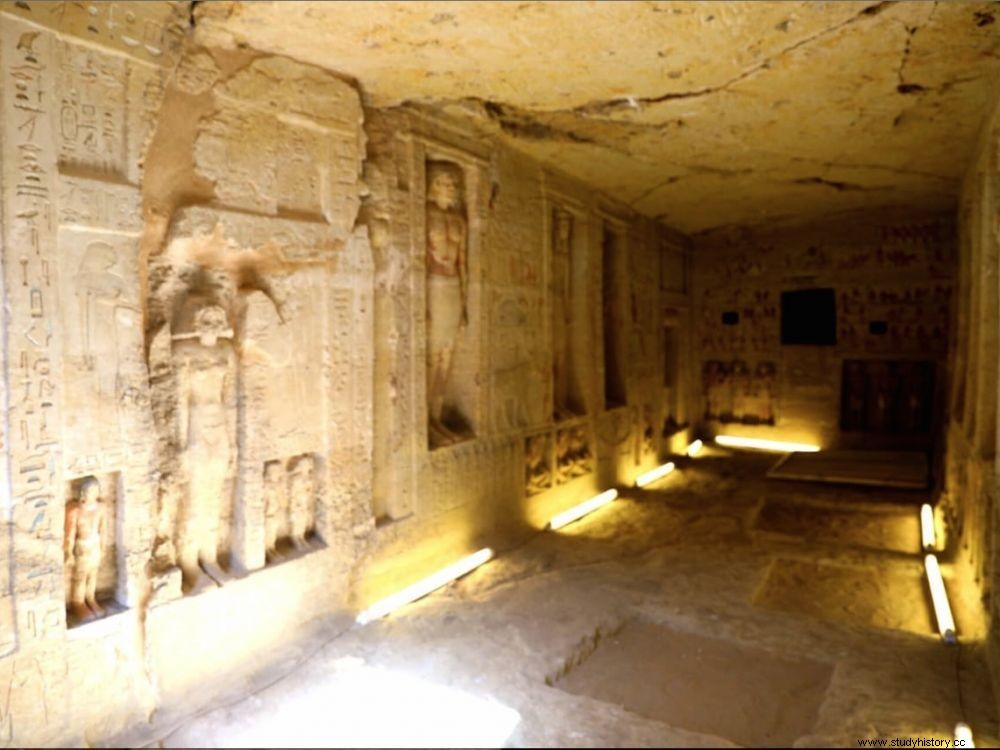

The tomb of the priest named "Wahtye" dates from the 5th Dynasty (between 2,500 and 2,300 BC), during the reign of Pharaoh Neferirkare.
The tomb of the priest named "Wahtye" discovered in Egypt dates from the Fifth Dynasty (between 2,500 and 2,300 BC), during the reign of Pharaoh Neferirkare (2446 - 2438 BC), according to the ministry of Antiquities. The tomb is "exceptionally well preserved, colorful with carvings inside. It belongs to a high-ranking priest ", rejoiced Saturday, December 15, 2018 the Minister of Antiquities, Khaled el-Enany in front of an audience of guests and the press. Wahtye indeed bore the title of "divine inspector" .
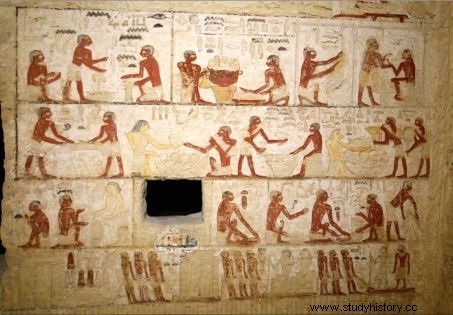
The tomb notably contains "scenes showing the owner of the tomb with his mother, his wife and his family, as well as a number of niches with large colored statues of the deceased and his family ", specifies the ministry in a press release. The niches are 18 in number and the statues 24, according to the same source which also specifies that the lower part of the tomb contains 26 smaller niches.

© Egyptian Antiquities Ministries
Most of these statues, ranging in size from 1 meter to human height, depict people or deities.
© Egyptian Antiquities Ministries
Some hieroglyphs found in the tomb refer to Wahtye's mother and wife. Others mount Egyptians engaged in various activities (cooking, drinking, construction...)
The team responsible for the discovery will now continue their investigations to try to discover the sarcophagus of "Wahtye".
In November 2018, on the same site of Saqqara, the Egyptian authorities revealed the discovery of seven tombs, including four dating back more than 6,000 years, by the same Egyptian archaeological mission. Archaeologists had unearthed beetles and mummified cats. The site of Saqqara, south of Cairo, is a vast necropolis which notably houses the famous step pyramid of Pharaoh Djoser, the first of the Pharaonic era. This monument, built around 2,700 BC by the architect Imhotep, is considered one of the oldest monuments on the surface of the globe.
