Before we dive into the history of space exploration, let's look at what great people have said about space.
"Many years ago, the British explorer George Mallory, who was to die on Mount Everest, was asked why he wanted to climb it. He said, "Because it's there." Well, space is there, and we are going to climb it, and the moon and the planets are there, and new hopes of knowledge and peace are there. ”
John F Kennedy
John F Kennedy, was the US President between 1961 and 1963.
"Two things inspire me to awe - the starry sky above and the moral universe within."
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was a well-known German scientist, whose contributions were mainly in physics and quantum mechanics. He was born on March 14, 1879 and left the world on April 18, 1955.
Astronomy
Apparently, the idea of space exploration is not new to humanity. Ever since our ancestors used astrology to predict human life, space has been an eternal part of humanity's curiosity. It is also a branch of science devoted to the study of planets, celestial bodies and the space of the physical universe, known as astronomy.

As we all know, the earth is a planet in the solar system. As shown in the picture above, it consists of the sun - the giant star, and eight planets, namely Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Pluto is another small planet-like (dwarf planet) object that is no longer considered part of the planetary system. However, our solar system is part of the Milky Way galaxy. And there are many such galaxies that make up the universe. Outer space, which lies outside the physical boundaries of the planet, consists of various other things such as comets, natural satellites, meteorites, stars, dust, and so on.
Glossary, just to get to know
- Astronaut - A person who is trained to travel in a spacecraft. A Russian astronaut is also known as a cosmonaut.
- Galaxy - A collection or system of a star and its orbits. For example, the Milky Way galaxy consists of a giant star, the sun and 9 planets orbiting the sun.
- Path - A defined path or path taken by any celestial body. For example, the moon revolves around the earth in a specific orbit.
- Planet - A non-luminous celestial body with a motion alone and with reference to a star. For example, the earth.
- Satellite - Any celestial object orbiting a planet. For example, the moon is a natural satellite, while GEOSAT is an artificial satellite.
- Star - A spatial object that burns and emits light energy. For example, the sun is a giant star.
The layers of the earth's atmosphere

The adjacent image shows the division of the earth's atmosphere at different distances above average sea level. As one can find out, the altitude is the planes or the hilltops when reaching about 20 km. It's the "Troposphere". Then comes the stratosphere at an altitude of 50 km where hot air balloons fly. This is followed by " Karman's line “. It is the boundary between the Earth's atmosphere and space. As we ascend to the height above the earth's surface, the density of air becomes thinner. Therefore, there can be no specific universal definition of this.
According to the generally accepted definition, there is still an imaginary line 100 km above the earth's surface. Beyond this point, the aircraft must travel at a higher speed to lift off and strike the earth's gravity. The first such object to cross the Karman line marking the beginning of space exploration was a V-2 rocket launched in 1944.
The Early History of Space Research
The machines launched in space to study the environment and collect samples are called probes. They can be of different types, depending on what we are aiming to explore in space. They are
- Crew / Crew / Pilot Probe - It carries astronauts
- Unmanned / unmanned / non-pilot probe - It does not carry humans
- Spaceflight / Spacecraft - An aircraft launched to travel in space to cross or reach
- Interplanetary Probe - These are launched over the solar system to reach a planet
- Room Station - A room type. It is a spaceship with a human crew that orbits the earth in the lower region for a long time.
Let's look at how things evolved and added to the story behind launching such different types of probes to explore space.
The Space War in the Cold War
World War II must be credited to the space research leap despite the wake it caused. It was the Germans who first launched a space missile. Although a "revenge weapon", the 200-mile V-2 missile / A-4 was used to attack London on September 8, 1944. It flew over 60 miles and attacked the various sites targeted by the German army.>
After Germany was defeated in World War II, the United States and the Soviet Union took over technology and designers. As it was the time when countries fought hard to prove their superiority over the other in all aspects, space exploration was no exception.
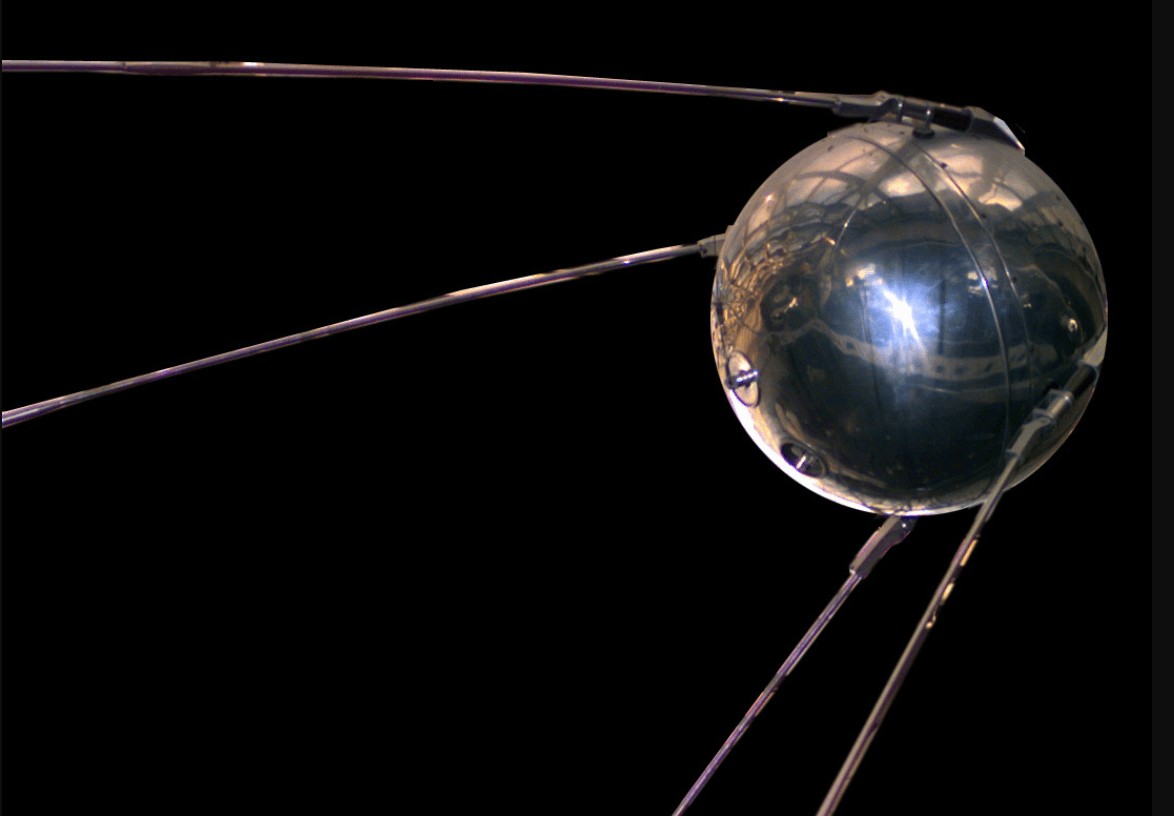

On October 4, 1957, the Soviets launched the first artificial satellite - 'Sputnik I', carried by an R-2 rocket into space. V-2 was a rocket aimed at the earth itself, while this was the first investment in the universe outside the earth. This orbited the earth in 96 minutes.
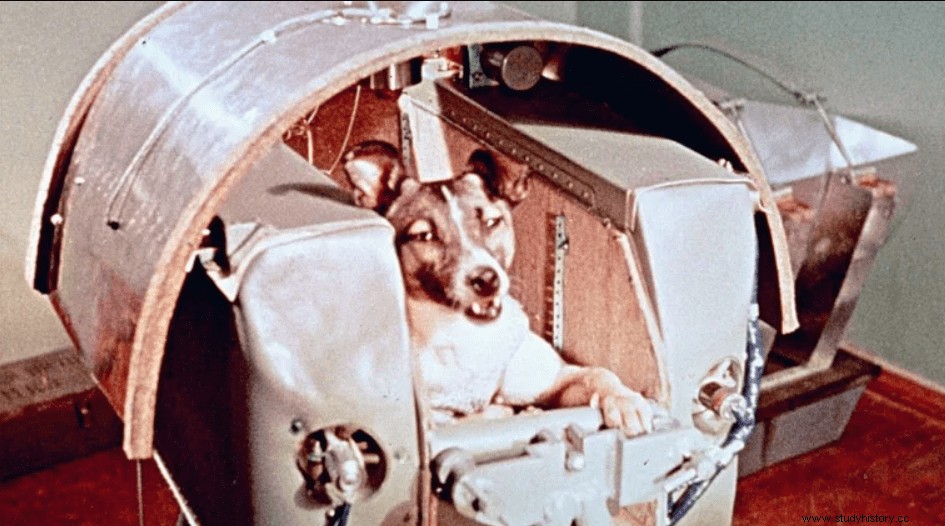
In a month's time, on November 3, 1957, the Soviets launched 'Sputnik II'. But it was an interesting satellite company that carried a living creature, a dog named Lika. This marks the launch of the first animal in space .
The United States declared the race against the Soviet Union
After a couple of failed launch attempts, the United States well into space on January 31, 1958 with a satellite called 'Explorer'. But it carried instruments to detect cosmic rays. Researcher James Van Allen started this study. Based on data from later satellites, we are now aware of what is known as the Van Allen belt around the Earth's atmosphere.
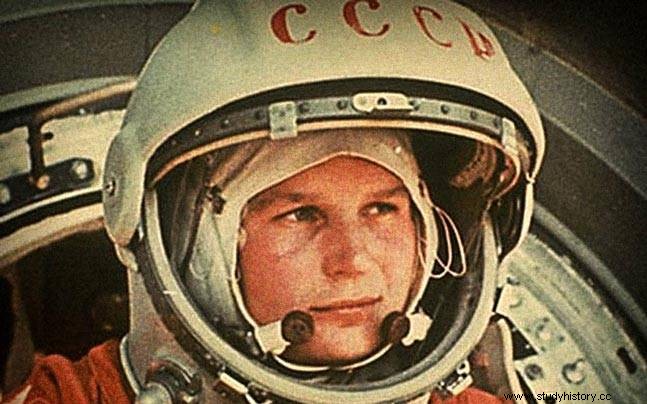
In October 1958, NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) was formed by the US government to make focused advances in space research. As early as April 12, 1961, Soviet astronaut Yuri Gagarin was the first man in space . He orbited the planet for 108 minutes in space travel called 'Vostok 1'.

In the face of the heat of the press, the United States declared itself a "Space Race" against the Soviet Union. Three weeks later, 5,1961. May 7, they launched a satellite called 'Mercury Spaceflight', also known as 'Freedom 15'. Alan Shepard, who flew into this, became the first American and second human in space. His plane, however, lasted only XNUMX minutes, and it was on a suborbital orbit, which means that the plane enters space, but does not go around the earth.
The big challenge
With the Soviets pioneering everything from the first satellite to the first man in space, US President John F Kennedy declared that the goal of the nation would be to touch the moon in a decade!
While the Soviets moved forward quickly in everything, the Americans had to drive up. But the Soviets continued to climb the ladder. They launched a 'Luna Series', with 'Luna 2' as the first man-made object to hit the moon in 1959. And then, the first automatic soft landing on another celestial body (moon) was obtained by 'Luna 9' on February 3, 1966. 'Luna 10' was the first artificial satellite to enter the lunar orbit on April 3, 1966.
To meet the enormous challenge posed by the president, NASA built "Project Gemini" in the 1960s. In this program, astronauts were trained to stay on long space travel. Then they launched "Project Apollo". In this series, it was "Apollo 11" that made America's dream come true on July 20, 1969. The mission succeeded in landing the first crew on a celestial body (moon) .Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin were the crew of the first astronauts to set foot on the Moon.
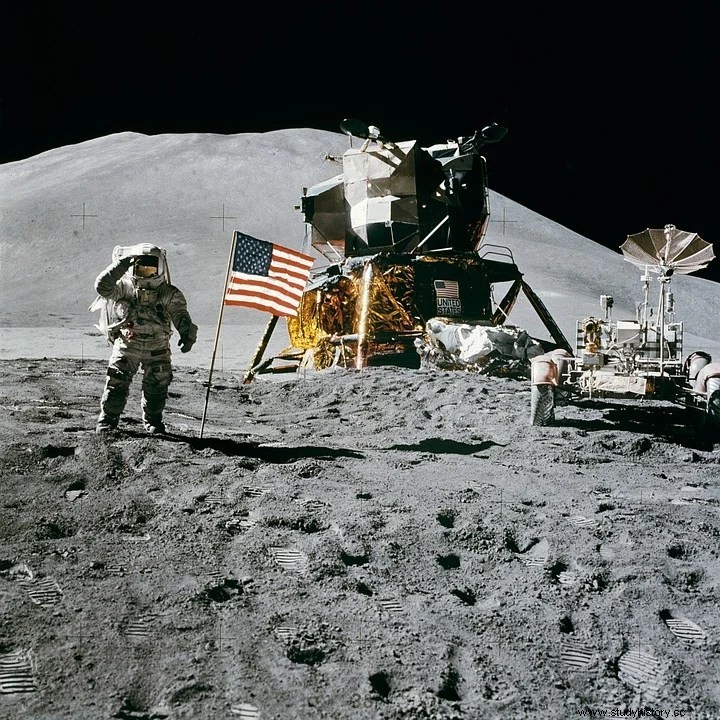
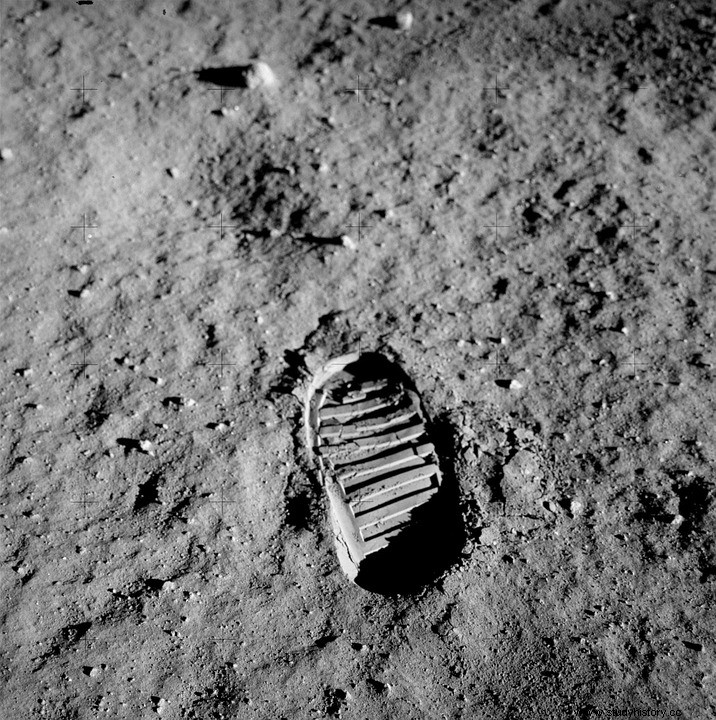
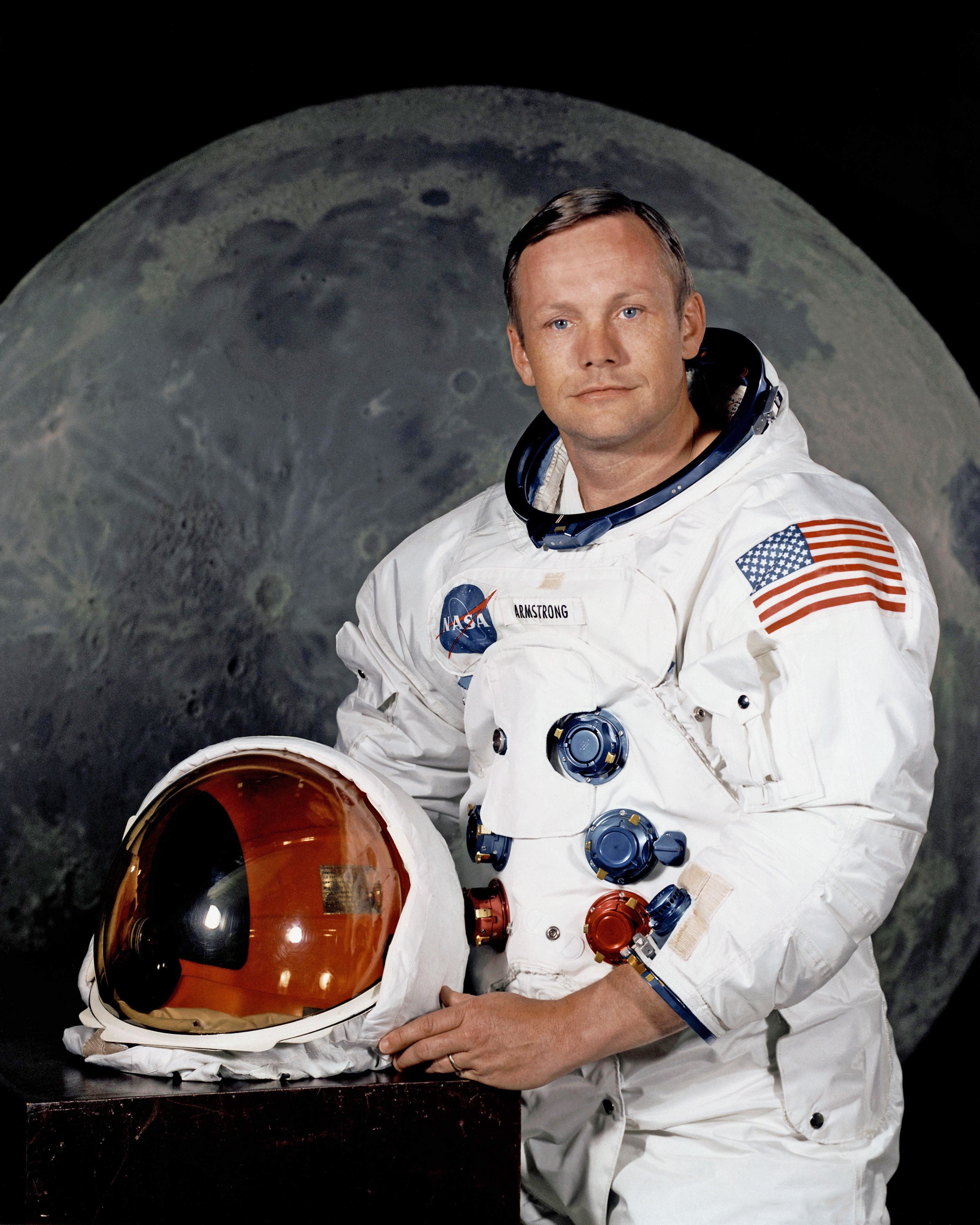



“It's a small step for (a) man; a great leap for humanity .. ”
- Neil Armstrong from the Moon
As a result of this success, there were six landings with crew on the moon of the United States between 1969 and 1972. Since then, pilot probes to space have been limited to only within the low orbit of the Earth.
Interplanetary missions
These are of two types, namely flyby or orbiter missions and surface missions. In the former, the launched probes will pass the planet or orbit the planet. While in the latter, the probe will enter the planet's atmosphere, land on the surface of the planet and return data as images.
The first successful flyby missions from NASA
| Probe | Target | Release Date |
| Mariner 2 | Venus | August 27, 1962 |
| Mariner 4 | March | November 28, 1964 |
| Pioneer 6 | Bane solen | December 16, 1965 |
| Pioneer 10 | Jupiter | March 2, 1972 |
| Pioneer 11 | Saturn | April 6, 1973 |
| Mariner 10 | Mercury | November 3, 1973 |
| Voyager 2 | Uranus | August 20, 1977 |
| Voyager 2 | Neptune | August 20, 1977 |
| New Horizon | Bane Pluto | January 19, 2006 |
| Dawn | Bane Ceres | September 27, 2007 |
The first successful surface missions from the Soviets
| Probe | Target | Release Date | Important Notes |
| Venera 7 | Venus | August 17, 1970 | Returned data from Venus to Earth in 23 minutes December 15, 1970 |
| Venera 9 | Venus | June 8, 1975 | Pictures of the surface of Venus were sent on October 22, 1975 |
| March 3 | March | May 28, 1971 | Orbiter and Lander after soft landing December 2, 1971 stopped data transfer after 20 seconds |
Other notable missions
MOM , Mars Orbiter Mission or Mangalyaan was launched by ISRO, India, making it the first country to make a successful maiden attempt in the world. In addition, it was the cheapest (almost half the amount that would cost a Hollywood film production) and a light spacecraft (carried by PSLV and not GSLV) that was launched on November 5, 2013. It successfully entered the Mars orbit in September 24, 2014. It is still in operation, making it the fourth nation after NASA, Russia (Soviet Union) and Europe to have succeeded in the mission. There is also a movie called "Mission Mangal" in Hindi that was loosely based on this challenging mission.
EVA- Extravehicular activities are those performed by astronauts outside the spacecraft and outside the Earth's atmosphere. The main activity is "Space Walk". Alexei Leonov became the first man to go into space when he left Vokshod 2 on March 18, 1965, after it was launched by the Soviets. He went into space for 12 minutes and 9 seconds.
Space Stations
The first space station was launched
The Soviets launched the World's First Space Station in orbit with low ground April 19, 1971. The spacecraft known as "Salyut 1" was successfully launched. After three days, the Soyuz 10 - a manned probe, was launched to connect / connect to Salyut 1. But the docking failed, and the team returned to Earth.

After this, Soyuz 11 was launched with three astronauts 6,1971. June 23. After successfully docking and conducting experiments for 29 days, the crew returned to Earth XNUMX. June. Unfortunately, due to technical problems, they died while returning to Earth's atmosphere. They are the only people who have died outside Karman's line.
When Salyut 1 ended and landed on Earth, it burned up as it entered the Earth's atmosphere on October 11, 1971.
ISS:Maybe the end of the Space Race
Later, SkyLab by America, Salyuts 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and Mir were launched by Russia as individual space stations, each lasting a few years. Later, ninth in a row, the International Space Station (ISS) was launched. It was the result of cooperation between the United States, Russia (formerly known as the Soviets), Japan, Canada and Europe.
The ISS spacecraft took off from American land on November 20, 1998. It was first anchored with a six-member crew on December 4, 1998. Lives for over 22 years now, making it the longest mission in space ever continuously inhabited by astronauts. To date, around 240 astronauts from 19 countries have visited the ISS. Some have gone many times too.
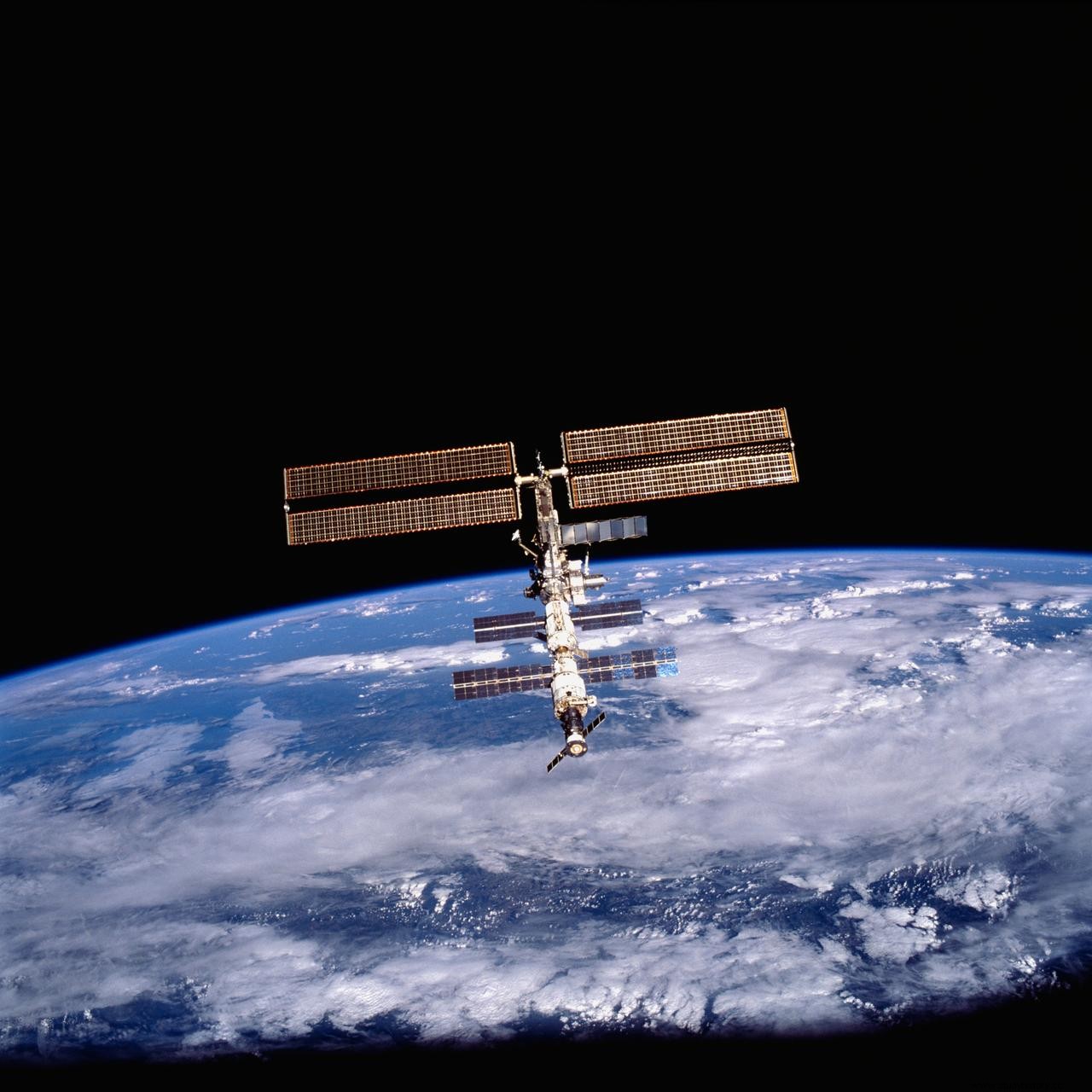


The ISS is the largest manned spacecraft orbiting the Earth in a low orbit area. It is the third generation module station, ie it can be modulated and thus changed. Each of the modules can be removed or added. Research, experiments and studies in various fields have been going on since the beginning of space.
Current Events / Highlights
Although the space research fleet was initially hugely dominated by the United States and Russia, several countries began to share the carving of their space in the space exploration journey. This can be attributed to the fact that most countries after World War II were directly or indirectly affected by it apart from the winning powers. Either they recently became independent of colonialism, or they lost the war.
Today, some of the key players include the United States (NASA), Russia (ROSCOSMOS - Roscosmos State Corporation for Space Activities), Japan (JAXA - Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), Europe (ESA - European Space Agency), Canada (CSA - Canadian Space Agency) , China (CNSA - China National Space Administration) and India (ISRO - Indian Space Research Organization). There are many other nations with their own individual government organizations for space research and research.

To mark a few upcoming space events, NASA is looking at making a spacewalk with the latest rapid team of astronauts. ROSCOMOS is developing and testing a Soyuz-2 launch vehicle to replace the existing Soyuz family that was used for various orbital launches; low, medium, very elliptical, solar synchronous and geostationary. JAXA helps the development of a crew jet with pressure (a machine that goes on the surface of the celestial body after landing).
The future of the unlimited space
After the world wars and the Cold War, the world comes together to search for an alternative habitat for humanity. It is good to see that space organizations around the world are joining forces to achieve their common goal. Instruments and parts of launch vehicles are manufactured by one country, they are all assembled and tested elsewhere, and it is eventually launched from another country.
In this way, all nations work as a team. Lately, there are interesting "Space Tourism" programs popping up. Buying land on the moon and building a house on Mars has become a popular buzz word these days. Because ongoing research is heavy on exploring the Moon and Mars to transport humans in the future.
In the journey to space research, we may end up getting answers to questions such as "How did the universe and the earth come to be?". It may shed light on some exciting theories of science such as dark matter, black holes, microgravity. We can use resources from other planets to survive on Earth or start living on other celestial bodies.
