On November 11, 1918, World War I came to an end. The German government signed the surrender, accepting all the victors' impositions.
Afterwards, the victors met in Versailles, France, where they discussed the terms of the Treaty of Versailles.
Main Consequences
The First World War left thousands of dead, changed the European map and the way of doing diplomacy.
Human and Material Losses
The war killed nearly 13 million people and left 20 million injured and maimed.
Powerful weapons were used in this conflict:asphyxiating gases, long-range cannons, machine guns, flamethrowers, tanks, planes and submarines. Many were first used in a war.
Even the victorious countries had lost much of their young male population and those who returned from the war were maimed or seriously mentally challenged. The material losses were also enormous and roads, bridges, entire cities had to be reconstructed.
A period of decline in Europe began, with the social problems of unemployment, hunger and misery. Political and social instability favored the emergence of totalitarian regimes.
Faced with this situation, societies were apprehensive about the possibility of a new world conflict of greater proportions and consequences than the first, which in fact happened with the Second World War.
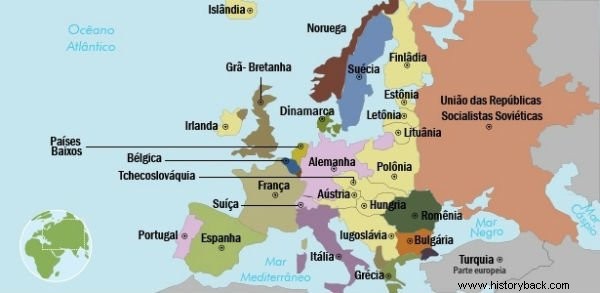
New Countries
Four empires that were considered solid before 1914 simply collapsed:German, Austro-Hungarian, Russian and Ottoman.
With the Treaty of Versailles, from the ruins of these empires, new countries emerged such as Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Austria, Hungary, Estonia, Lithuania and Latvia.
The Ottoman Empire saw its borders diminish. The modern state of Turkey emerged, which had to recognize Armenia's independence. It was up to France and England to administer the territories of Syria, Lebanon and Iraq under a mandate.
 See also:Eastern Europe
See also:Eastern Europe League of Nations
The creation of the League of Nations in January 1919, based in Geneva, Switzerland, was inspired by the peace proposals of American President Woodrow Wilsoon.
The aim was to get nations to diplomatically discuss their problems before going to war.
United States
The United States was the big winner of the conflict.
They traded for more than three years with the Allies, did not see their territory being invaded by enemies and still became creditors of European nations.
Their industries would not suffer competition from Europe and their losses were few compared to those of their European partners. For all that, the country would continue its rise as a world power.
World War I - All MatterRead Also :
- World War I
- Main Battles of World War I
- Causes of World War I
- Phases of the First World War
- Brazil in World War I
- Trench Warfare
- Questions about the First World War
- Films about the First World War
- Beginning of World War II
