The word Mesopotamia means "between two rivers" and refers to the city-states, empires, and civilizations that arose between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
The Mesopotamian civilization is called the "cradle of Humanity", because there lived peoples who left to humanity legacies such as the division of the calendar into 360 days, writing, astronomical calculations, among other inventions.
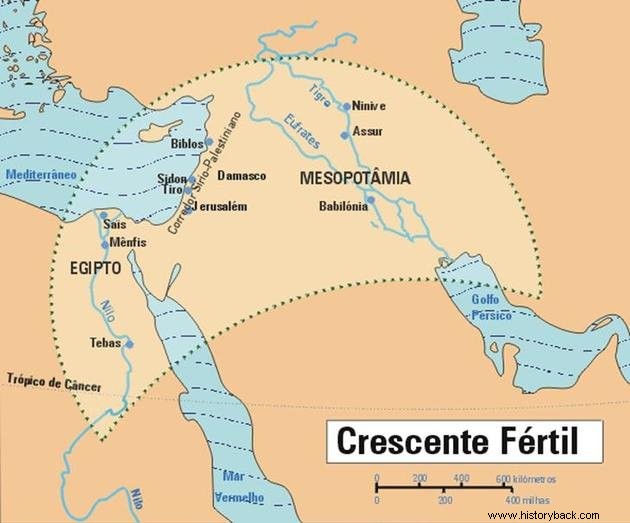
Mesopotamia:location and map
Mesopotamia was the word the Greeks used to indicate the lands between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Currently, it corresponds to the northern territories of Syria and much of Iraq, ending in the Persian Gulf.
Formation of Mesopotamian Civilization
Around 10,000 BC, the first humans settled in the region of Mesopotamia, developed agriculture and domesticated the first animals. Thus, the human being stopped being a nomad to become sedentary.
This zone had fertile land and extended as far as Egypt. Its extent, when traced on a map, resembled the crescent moon and was therefore called the Fertile Crescent.
The more food, the more people could eat and live better. Now, human beings organize themselves into cities. On the other hand, as the population grew, more space for cultivation was also needed and so began the disputes over territory.
However, despite the fights over land, the different cities began to trade with each other, with the surplus of their crops. Therefore, there was a specialization of tasks among the population and this started to be divided between farmers, warriors and traders.
There were also those who had the key to the sacred, the priests and priestesses. Thus, the idea of religion appears, around the year 6000 B.C.
With the growth of cities and commercial exchanges, the need to control the products that came in and out arose. Thus, the writing system begins, first with pictorial symbols, and later with simpler drawings.
The development of writing marks for many scholars the end of prehistory. The later period is called Antiquity.
See also:History of WritingMain Cities of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia was the birthplace of great cities. We cite some as:
- Ur
- Uruk
- Nineve
- Acadia
- Babylon
- Babel
Mesopotamian Civilization

The area between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers was occupied, about 5000 years ago, mainly by two peoples:the Sumerians, to the south, and the Akkadians, to the north.
Around 3000 BC significant changes began in that area with the growth of cities and the establishment of the monarchy as a form of government.
The first king to unify the different cities in Mesopotamia was Sargon I. Under his reign, the Mesopotamian cities ceased to be rivals with each other and formed a vast empire, the first created in the history of mankind
Likewise, the grandson of Sargon I, Narâm-Sîm, was the pioneer in declaring himself a divine being and establishing a cult in his person. Around the year 2200 BC, this Empire ends due to the invasion of the Guti peoples.
See also:Peoples of MesopotamiaSummary of Mesopotamian Civilization
The peoples who lived in the Mesopotamian region gave humanity inventions that are used all over the world.
From astronomical calculations, to the idea of locking houses with keys, the societies that developed in that area created:
- Agriculture and temple building;
- Unified weights and measures system;
- Administrative division of the kingdom into provinces;
- Tax payments in the form of part of the harvest;
- Division of the year into 360 days and the week into seven days.
See also:Mesopotamian Civilization Research this topic too:
- Division of History
- Sumerians
- Chaldeans
- Akkadians
- Questions about Mesopotamia
