It is considered a pharaoh those leaders who reigned in Egypt, after the unification of Lower and Upper Egypt carried out by Menes. This king ruled from 3185 to 3125 BC
The Life of a Pharaoh it was marked by religious rituals, meetings with his advisors, reception of ambassadors, visits to works and plantations.
The first Pharaohs

Power passed from father to son, but court intrigues could disrupt the line of succession, favoring relatives and even noble families.
As they led Egypt for over 3000 years, it is evident that their daily lives varied. The first kings even passed a physical aptitude test every year to show that they could stay in office.
Although it is well known, the title of “pharaoh” was given by the Hebrews and later popularized by the Greeks. Only later was it adopted by the kings of Egypt.
Life of Pharaoh
The life and rule of a pharaoh were guided by religion. When they ascended the throne, the first thing they did was build graves for themselves and their family.
The best known of these tombs are the pyramids that have survived to this day and are considered one of the 7 Wonders of the Ancient World.
See also:The Pyramids of EgyptEducation of the Pharaoh
The formation of the crown prince varied according to the time. Many pharaohs probably could not read or write, as this function was left to scribes.
However, they learned the necessary rituals to worship each god, to perform the correct gestures in the ceremonies and, mainly, the prayers to be said.
Also knowledge of astronomy and mathematics were taught to future sovereigns.
See also:Egyptian MythologyRoutine of a Pharaoh
A common day in the life of a pharaoh included visits to temples and sacrifices to the gods, but also meetings of a governmental nature.
To start the journey, the pharaoh bathed and was massaged with ointments and perfumes that left him fragrant. Their garments were made of linen and their ornaments were usually of gold, precious or rare stones. All with the intention of highlighting his features and his power.
When going out to visit some building or plantation, the pharaoh was followed by a crowd that tried to approach his sacred person. Carried on a litter, in order to be seen by the population, the pharaoh reinforced his power as an intermediary between the gods and human beings.
Only in the afternoon could the pharaoh enjoy its palaces and stroll through its gardens. However, at sunset, a ceremony held to thank the gods required their presence again.
See also:Egyptian CivilizationSacrifice to the gods
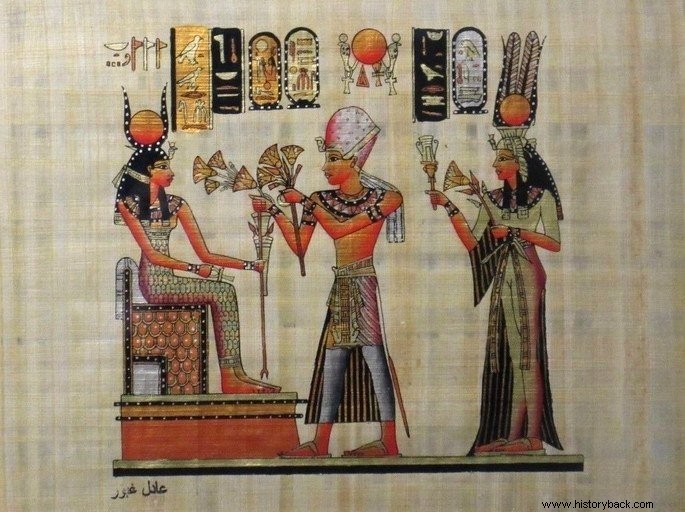
Considered to be the incarnation of the god Horus, or another god of the Egyptian pantheon, a pharaoh had to offer daily sacrifices to the gods in order to guarantee his people the blessings of the deities.
Plentiful harvests, victory in wars, end of epidemics, flooding of the Nile River, all this should be ensured through the cult performed by the pharaoh.
See also:Egyptian GodsCoronation of a Pharaoh
A Pharaoh's coronation ceremony lasted about five days and was held in Memphis. This was the city that the first pharaoh, Menes, had been crowned with and thus his successors maintained the tradition.
The pharaoh received attributes of power such as the double crown that represented Lower and Upper Egypt, the staff and the scourge (a kind of whip). From then on, he was considered a deity on earth and made a sacrifice in honor of the god Ptah.
Most important pharaohs
Thirty dynasties took turns on the throne in a period from 3100 BC. to 332 BC
Thus, many Egyptian rulers stood out for their political, military or because they left large buildings.
Below are some great kings of Ancient Egypt:
Menes (or Narmer)
He was the first leader to reign in Lower and Upper Egypt, between 3200 BC. and 3000 BC. He founded the city of Memphis, started the cult of various gods and knew how to govern skillfully so as not to displease the two regions of his territory.
See also:Ancient EgyptTutankhamun
He reigned from 1333 BC. and 1323 BC. He restored the polytheism abolished by the father and Thebes as the capital of Egypt. His figure is not so remembered for his years of rule, but rather because of the fabulous find of his tomb in 1922, which brought a new perspective to Egyptology.
See also:TutankhamunRamesses II
He ruled 66 years from 1279 to 1213 BC. C. One of his wives, Nefertari, played an important political role during his long reign. A great builder, he established a new capital called Pi-Ramses. However, he had to let the Hebrews go in the face of the plagues that ravaged Egypt.
See also:Ten Plagues of EgyptCleopatra
Despite the succession being made only by male descendants, some women sat on the Egyptian throne, as regents or sovereigns. One of them was Cleopatra VII, who reigned from 51 BC. until 30 BC, and guaranteed a privileged position for Egypt within the Roman Empire.
See also:Cleopatra There are more texts on this topic for you :
- Egyptian Art
- Sphinx of Giza
- The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
- Theocracy
