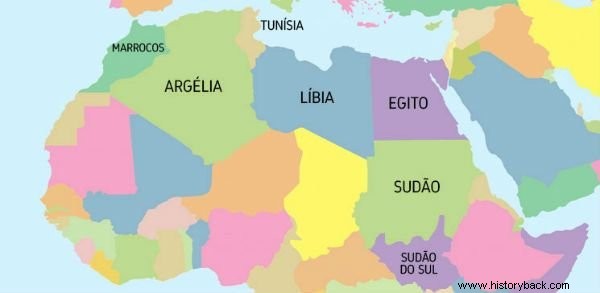
The North Africa , North Africa or North Africa, is made up of seven countries:Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Sudan, South Sudan and Tunisia.
There is located the second largest desert in the world, the Sahara, which has approximately 9 million km 2 extension.
It is worth remembering that the African continent is divided into 54 countries distributed in five regions:
- North Africa (North Africa or North Africa)
- West Africa
- Central Africa
- East Africa
- South Africa
Map
See on the map below where the countries of North Africa are located:
General Data
- Borders: Mediterranean Sea, Atlantic Ocean and Spain (Morocco).
- Predominant religion: Islam.
- Largest country by land area: Algeria.
- Smallest country in territorial extension: Tunisia.
- Most populous country: Egypt.
- Most industrialized country: Egypt.
- Economy: Agricultural, livestock, tourism and oil.
- Independence: Algeria - July 5, 1962; Egypt - June 22, 1952; Libya - January 1, 1952; Morocco - March 2, 1956; Sudan - January 1, 1956; South Sudan - July 9, 2011; Tunisia - March 20, 1956.
Algeria

- Capital :Algiers
- Approximate territorial extent :2,381,740 km²
- Language :Arabic, Berber and French
- Currency :Algerian Dinar
- Population: 39,928,947
Algeria's history dates back to two thousand years before Christ, when its region was disputed by western civilizations.
Phoenicians and Carthaginians joined to fight the invasions, until it is invaded by the Romans.
With the fall of the Roman Empire, centuries later Algeria is occupied by the Vandals, who destroy what the previous ones had built.
After the Arab expansion, it was France's turn to invade the country and make it its colony in the period between 1830 and 1962. Algeria's independence from France dates from July 5, 1962 and was achieved through a bloody war.
Egypt

- Capital :Cairo
- Approximate territorial extent :1,001,450 km²
- Language :Arabic
- Currency :Egyptian pound
- Population :83,386,739
Egypt carries one of the oldest histories in the world, dating back to around eight thousand years before Christ.
Elements of their culture are legacies that survive to this day, especially the writing and construction of the pyramids.
The Egyptian people excelled in the development of Mathematics, Medicine and Astronomy.
The Egyptians became a reference on a cultural and commercial level. Its decline began and accentuated at the end of the 20th century after the creation of the State of Israel in 1948.
Read more:
- Ancient Egypt
- Pyramids of Egypt
- Egyptian Civilization
Libya

- Capital :Tripoli
- Approximate territorial extent :1,759,540 km²
- Language :Arabic
- Currency :Dinar
- Population :6,253,452
Libya was also conquered by the Romans and later invaded by the Arabs. It became an Italian colony, which provided improvements for the country. Libya's independence was won on January 1, 1952.
The exploration of oil, discovered in the late 1950s, triggered the beginning of conflicts. It was from there that Libya tried to unite with other countries, without success.
Like Egypt, Libya is at the center of the conflicts that began in 2010 in Tunisia, a movement known as the Arab Spring.
Morocco

- Capital :Rabat
- Approximate territorial extent :446,550 km²
- Language :Arabic, French and Spanish
- Currency :Dirham
- Population :33,492,909
Before the Spanish and French divided the country, Morocco was in the hands of the Berbers, Carthaginians, Romans, Vandals and Byzantines.
Morocco was a Spanish colony, as well as a French one, and on March 2, 1956, Spain and France recognized their independence. The country claims the territory of Western Sahara, a former Spanish possession.
Morocco's economy is mainly governed by tourist activity.
Sudan

- Capital :Khartoum
- Approximate territorial extent :1,861,484 km²
- Language :Arabic
- Currency :Sudanese Pound
- Population :38,764,090
The independence of Sudan, which was a British colony, dates from January 1, 1956. Before, however, Egypt had conquered it.
In 2011, South Sudan became independent. Until that year, Sudan was the largest country on the African continent, but it lost that status due to its division that gave rise to South Sudan.
Sudan and South Sudan are in civil war, so it is a very unstable country in terms of security.
South Sudan

- Capital :Mane
- Approximate territorial extent :644,329 km²
- Language :English and Arabic
- Currency :South Sudanese Pound
- Population :11,738,718
Rich in oil, South Sudan, also known as the “New Sudan” - due to the division with Sudan in 2011 - is one of the most precarious countries in the world.
There, there is a shortage of food, medical care, lack of education, high infant mortality rate, among others.
Tunisia

- Capital :Tunes
- Approximate territorial extent :163,610 km²
- Language :Arabic
- Currency :Tunisian Dinar
- Population :11,116,899
Colonized by the Phoenicians, Tunisia was an important element of the commercial area. After the Phoenicians, the Arabs made the country stand out, this time in religious terms.
Years later, it was France's turn to invade the territory until Tunisia formed a sovereign state in 1956. It is in this country - the smallest in the North African region - that the Arab Spring begins.
Middle East
The Middle East, also called Western Asia, occupies part of North Africa. Among the main cities in this region is Cairo - capital of Egypt, which is located between North Africa (most of it) and part of Asia.
See also:Middle EastArab Spring
It all started when a young man in Tunisia set himself on fire in protest at the closure of his fruit stand. The bank, which was his source of income, had been shut down by the police.
The people revolted, leading President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali (1936) - who had ruled the country for more than 20 years - to leave the country the following month.
The satisfactory result of the popular uprising influenced the people of Libya. There there was a violent movement that ended up killing Muammar al-Gaddafi (or Gaddafi), two months after the start of the civil war. Gaddafi was the country's president from 1969-2011
In Egypt, in less than a month, the people also managed to overthrow the government of President Hosni Mubarak (1928) who had been in office for 30 years.
The action was reflected in other countries in the region. In Algeria, for example, people are demanding jobs and the possibility of obtaining a visa to leave the country.
See also:Arab SpringRead more :
- Africa
- African Culture
- Arab Culture
- Sahara Desert
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Countries of Africa
- Decolonization of Africa
