The Vikings were a people of northern Europe who conquered territories in England and France during the High Middle Ages.
They are among the main cultural references of Scandinavia and to this day we can find representations of the Vikings in films and television series.
Location and territorial expansion
Vikings lived in present-day territories of Greenland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark and Finland. We call the “Viking Age” the period between the years 800 to 1100, when they expanded beyond these borders.
From the 8th century onwards, the Vikings began to leave their territory in search of new lands.
They invaded and settled mainly in Iceland and the UK, as we can see in the map below:
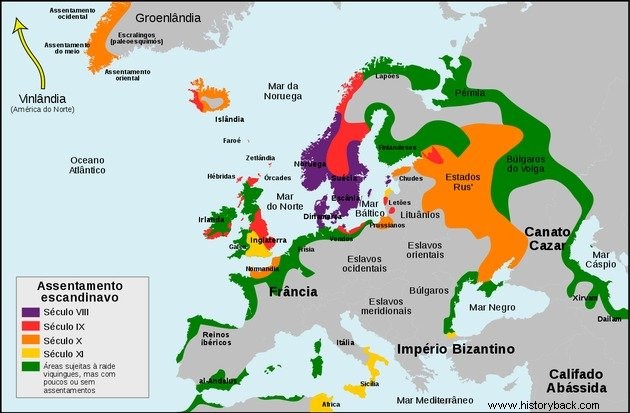
The Vikings who settled in northern France were called Normans and invaded England in the 11th century. This domination ended with the English king Henry II in 1154.
See also:ScandinaviaWho were the Vikings?
It must be remembered that the Vikings were not a homogeneous people, but several tribes and clans that adopted similar customs and languages. Some historians call them "Nordic people".
The behavior of Vikings abroad was often quite brutal and attacks such as that of the Lindisfarne monastery in 793 are cited as proof of this violent character.
However, if we compare with other peoples of the time, we will see that they followed the same standards of conduct.
Viking social organization
Viking society was organized into well-defined social strata. At the top were the large landowners, in the middle were the farmers and at the bottom were the slaves.
There were also the great divisions between the free and the unfree, the rich and the poor, as well as between men and women.
The Vikings were ruled by a king, however, not in the way we understand a monarch today.
The right to reign was not hereditary and candidates had to fight each other to win the crown. Thus, it was essential to make alliances through marriages and gather loyal men around the candidate for king.

Viking economy
Land and agriculture were of fundamental importance to ensure high social status. However, the Vikings also sailed the European seas and traded with neighboring peoples.
The Vikings' success at sea is explained by their experience in building fast and seaworthy boats. This took them to Russia, the Byzantine Empire and even America 500 years before Columbus.
Viking culture
Viking art was extremely elaborate. Navigators and jealous warriors, the Vikings used to make reliefs with plant and animal motifs on the hull of their boats. The weapons and helmets were also richly carved with designs that signified both social status and protection.
We can find inscriptions made with runes, the alphabet used, on carved stones, everyday objects, as examples of Viking art.
Likewise, high society women used to adorn themselves with jewelry and amulets made from the most varied materials such as animal bones and turtle shells.
Viking Mythology
The Vikings, like other peoples of the time, worshiped a series of gods related to the phenomena of nature.
One of the main ones was Thor, possessor of a hammer with special powers. His worship was performed in the forests through trees like the oak, by the rivers and the sea.
Although the god Thor occupies an important place in the Norse pantheon, the truth is that there were specific gods for each situation in everyday life.
Some Norse Gods were:
- Odin - the father of all, lord of life and death, magic and prophecy.
- Frigga/Freya - the wife of Odin, protector of the family, goddess of fertility.
- Thor - son of Odin, the god of thunder, his symbol was the hammer, much worshiped in Iceland.
- Baldr - son of Odin, god of intelligence and beauty.
- Valkyries - were minor goddesses charged with leading the spirits of warriors killed in battle to Valhalla, where they would serve Odin and Freya.
Today, this religion is reappearing in Scandinavian countries and in Great Britain.
Curiosities
- Although widespread, there is no material evidence that the Vikings wore horned helmets.
- Also the custom of drinking wine on the skull of enemies is attributed to a translation error and does not correspond to reality.
We have more texts on the subject for you:
- Nordic Countries
- Paganism
- Barbarian Peoples
- High Middle Ages
- United Kingdom
