The Holy Roman Empire was a monarchy of feudal character that lasted from 800 until 1806 in Central Europe and part of Northern Europe.
At its height, it included the current territories belonging to Germany, Austria, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic.
It also included Slovenia, the eastern part of France, the northern part of Italy and western Poland. It constituted a hundred counties, duchies, principalities and imperial cities.
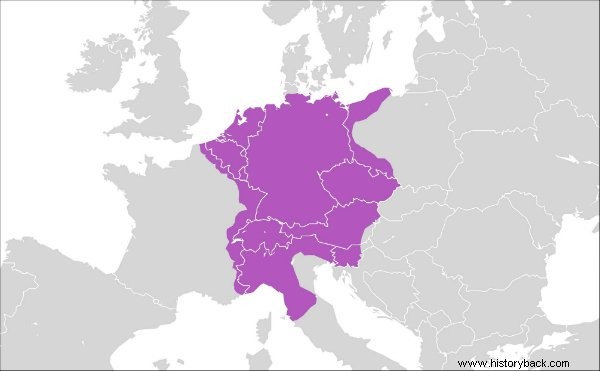 Territory coverage at the height of power of the Holy Roman Empire
Territory coverage at the height of power of the Holy Roman Empire
Charles the Great and the Carolingian Empire
The creation of this multilingual empire began in 800, the year of the coronation of Charlemagne by Pope Leo III. The act represented the restoration of the Western Roman Empire. It was the beginning of the Carolingian Empire.
The conglomerate resulted from the dissolution of the Frankish Empire, following the Treaty of Verdun, signed in 843. The empire was dissolved in 1806, as a result of the Napoleonic Wars. At that time, it covered the territories that today belong to Belgium, Croatia, Italy, the Netherlands, France and Poland.
Understand this topic better. Read :
- Charles the Great
- Carolingian Empire
- Treaty of Verdun
Policy
The political unity defended by Charlemagne was based on Christianity. The Carolingian dynasty lasted until the death of Charles the Fat in 887. In his place, Otto I, the first Emperor of the territory known as the Holy Roman Empire, is crowned.
Otto I was Duke of Saxony, King of Germany and Italy. The coronation, presided over by Pope John XII, only took place with the guarantee of the independence of the papal states.
Society
The empire was an elective monarchy. The coronation of the Emperor was subordinate to the Pope and remained among the Germans until the dissolution.
It was divided into many territories ruled by noble heirs, prince-bishops or knights. The emperor was elected by a select group. Many regions maintained the successor's inheritance. So it was with the Habsburg dynasty, whose line of succession began in 1452 was not interrupted.
Complement your reading. See :
- Crusades
- Roman Empire
- Feudalism
Characteristics
- Division into territories and principality
- Regency was held by princes, counts or imperial knights
- Emperors considered themselves continuators of the Roman Emperors in defending the government and supporting the Church
- It was similar to a confederation
- Diverse ethnic composition
- Cultural Diversity
- Linguistic diversity
- Direct influence of the papacy
- Real power subject to divine authority
- Union of Church and State
- Feudal Production Mode
- Commerce had an administrative and judicial system
- City architecture focused on militarism
Lutheran Reformation
The movement started in 1517, by Martin Luther, practically imploded the model of the empire. The German's theses were used as a basis for questioning the emperor's power. Among the results are various conflicts, such as the Thirty Years' War (1618 - 1648), which left the empire devastated.
Other religious conflicts were fought in various locations in Europe. The result was the weakening of imperial power and redefinition of territories. The definitive end of the empire was a consequence of the Napoleonic Wars.
Keep studying! Read :
- Thirty Years War
- Protestant Reformation
- Napoleonic Wars
- Ancient Rome
- Roman Emperors
